ASSAY: A JOURNAL OF NONFICTION STUDIES
1.2
1.2
|
In her book The Situation and the Story, nonfiction writer and teacher Vivian Gornick claims that all works of literature contain both a situation and a story. “The situation is the context or circumstance, sometimes the plot; the story is the emotional experience that preoccupies the writer, the insight, the wisdom, the thing one has come to say” (13). Similarly, Philip Lopate addresses these distinct narrative threads as they pertain to memoir in his essay “Reflection and Retrospection: A Pedagogic Mystery Story”: “The trick, it seems to me, is to establish a double perspective that will allow the reader to participate vicariously in the experience as it was lived (the child’s confusions and misapprehensions, say), while benefiting from the sophisticated wisdom of the author’s adult self” (26). The dual perspective that Gornick and Lopate describe allows readers to experience scenes and anecdotes within a text from two vantage points— then and now. Essential to writing in this dual perspective are indicators of time: both the time the plot events took place (what Gornick refers to as the situation and Lopate calls the visceral experience), and the time the author is writing about and reflecting on those events (for Gornick, this is called the story; for Lopate, it is the intelligent narrator). The ‘then’ perspective must be clear enough in matters of chronology, expansion and concision of time, flashback and flash forward in order to keep readers firmly planted in a sequence of events. Simultaneously, the ‘now’ perspective must offer insight and depth of understanding in a way that accounts for the passage of time.
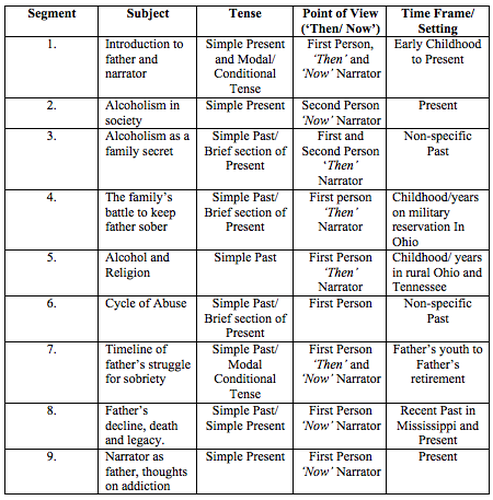
In his essay “Under the Influence,” acclaimed essayist Scott Russell Sanders navigates this dual perspective with great skill. To Sanders’ credit, the 10- page, 5700-word essay reads in a straightforward manner, but on close examination it reveals an elaborate construction and brilliant array of craft techniques, particularly in terms of narrative presentation and time control. Spanning over forty years, “Under the Influence” examines Sanders’ memories and experiences growing up with an alcoholic father; from how he experienced his father’s addiction as a child, to how it affects him now, as an adult. “Under the Influence” first appeared in Harper’s in November of 1989, but maintains popularity due largely to its inclusion in Philip Lopate’s The Art of the Personal Essay. Of Sanders, Lopate writes, “[He] threads his way through this minefield, so susceptible to cliché and victimized self-pity, with exemplary honesty, feeling, and willingness to take responsibility. His quiet Midwestern modesty and sense of privacy, seemingly at odds with an autobiographical genre that normally attracts flamboyant, self-dramatizing egotists, accounts for some of the essay’s tension—as though he would rather not write about himself, but the form demands it”. (732) Sanders’ success in avoiding the common pitfalls of melodrama and self-pity is at least partially the result of his ability to write effectively from both his ‘then’ and ‘now’ narrative perspectives.
Establishing Narrative Authority:
|
Click here to download a printable PDF with Works Cited.
|
Kelly Harwood is an artist and writer living in Boise, Idaho. She received her MFA in Creative Nonfiction from Vermont College of Fine Arts in 2015. Her work has appeared in Writers in the Attic: Detours Anthology, the forthcoming issue of Quaint Magazine, and on her blog, therosiepages.tumblr.com.
|
Related Works
|
Lynn Z. Bloom
Why the Worst Trips are the Best: The Comic Travel Travails of Geoffrey Wolff, and Jonathan Franzen 1.2 Articles |